데이터 불러오기
- 와인 데이터
- alcohol(알코올 도수), sugar(당도), pH(산도)
- class 0 = 레드 와인
- class 1 = 화이트 와인
1
2
3
| import pandas as pd
wine = pd.read_csv('https://bit.ly/wine_csv_data')
wine.head()
|
|
alcohol |
sugar |
pH |
class |
| 0 |
9.4 |
1.9 |
3.51 |
0.0 |
| 1 |
9.8 |
2.6 |
3.20 |
0.0 |
| 2 |
9.8 |
2.3 |
3.26 |
0.0 |
| 3 |
9.8 |
1.9 |
3.16 |
0.0 |
| 4 |
9.4 |
1.9 |
3.51 |
0.0 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-32f88054-395d-476e-b732-de1fe6fb312f button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-32f88054-395d-476e-b732-de1fe6fb312f');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 6497 entries, 0 to 6496
Data columns (total 4 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 alcohol 6497 non-null float64
1 sugar 6497 non-null float64
2 pH 6497 non-null float64
3 class 6497 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4)
memory usage: 203.2 KB
|
alcohol |
sugar |
pH |
class |
| count |
6497.000000 |
6497.000000 |
6497.000000 |
6497.000000 |
| mean |
10.491801 |
5.443235 |
3.218501 |
0.753886 |
| std |
1.192712 |
4.757804 |
0.160787 |
0.430779 |
| min |
8.000000 |
0.600000 |
2.720000 |
0.000000 |
| 25% |
9.500000 |
1.800000 |
3.110000 |
1.000000 |
| 50% |
10.300000 |
3.000000 |
3.210000 |
1.000000 |
| 75% |
11.300000 |
8.100000 |
3.320000 |
1.000000 |
| max |
14.900000 |
65.800000 |
4.010000 |
1.000000 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-b999d81a-0559-4b92-8e93-747feee74f33 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-b999d81a-0559-4b92-8e93-747feee74f33');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
표준화 작업
1
2
| data = wine[['alcohol','sugar', 'pH']].to_numpy()
target = wine['class'].to_numpy()
|
훈련데이터와 테스트데이터로 분리
1
2
3
4
5
| from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_input, test_input, train_target, test_target = train_test_split(
data, target, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 42)
print(train_input.shape, test_input.shape)
|
(5197, 3) (1300, 3)
1
2
3
4
5
| from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
ss = StandardScaler()
ss.fit(train_input)
train_scaled = ss.transform(train_input)
test_scaled = ss.transform(test_input)
|
모델 만들기
로지스틱회귀
1
2
3
4
5
6
| from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
lr = LogisticRegression()
lr.fit(train_scaled, train_target)
print(lr.score(train_scaled, train_target))
print(lr.score(test_scaled, test_target))
print(lr.coef_, lr.intercept_)
|
0.7808350971714451
0.7776923076923077
[[ 0.51270274 1.6733911 -0.68767781]] [1.81777902]
로지스틱 회귀
의사결정트리의 기본 알고리즘을 활용해서, MS, 구글 등 이런 회사들이 신규 알고리즘을 만듬
- XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost
- 캐글 정형데이터
- LightGBM (지금 현재 실무에서 많이 쓰임)
- 4월 말 까지는 코드에 집중 대회 나감
- PPT (알고리즘 소개)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
dt.fit(train_scaled, train_target)
print(dt.score(train_scaled, train_target))
print(dt.score(test_scaled, test_target))
|
0.996921300750433
0.8592307692307692
1
2
3
4
5
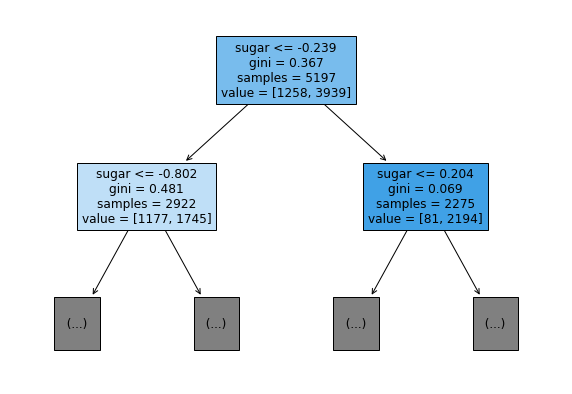
| import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.tree import plot_tree
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 7))
plot_tree(dt)
plt.show()
|

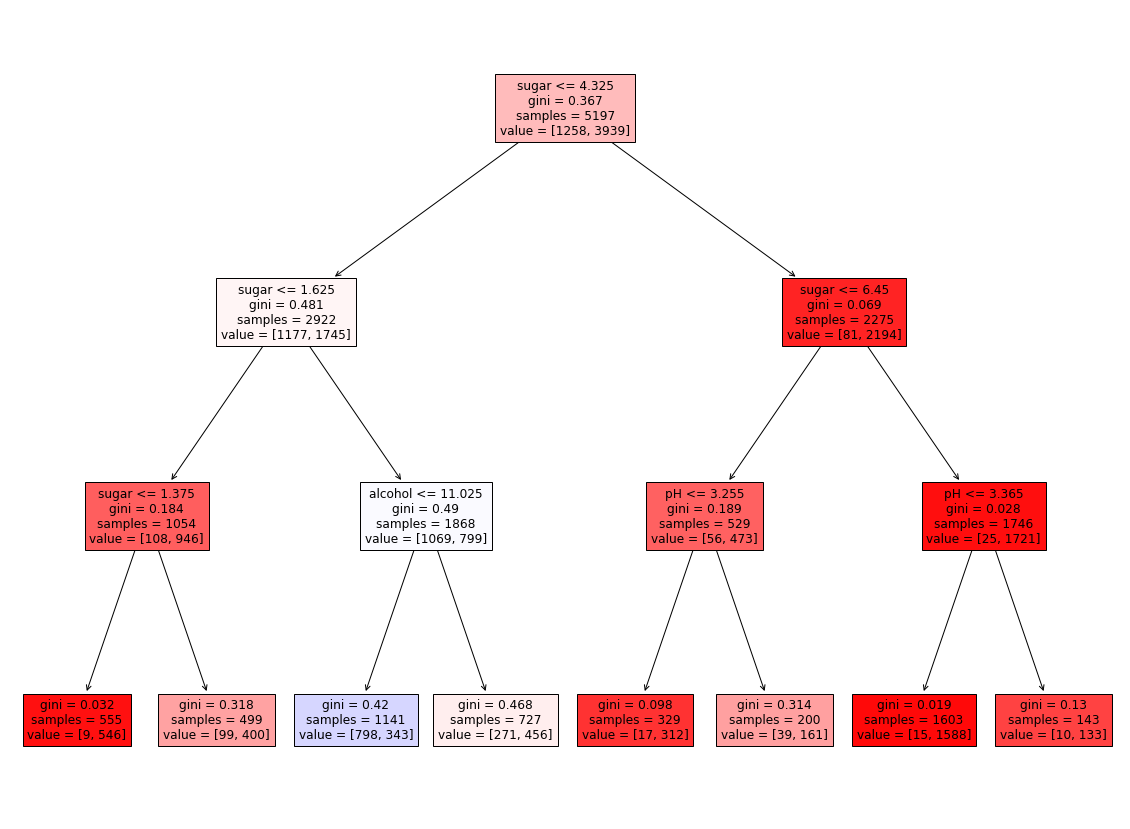
- filled = True
- 클래스 마다 색깔을 부여하고, 어떤 클래스의 비율이 높아지면 점점 진한 색으로 표시
1
2
3
| plt.figure(figsize = (10, 7))
plot_tree(dt, max_depth = 1, filled = True, feature_names = ['alcohol','sugar', 'pH'])
plt.show()
|
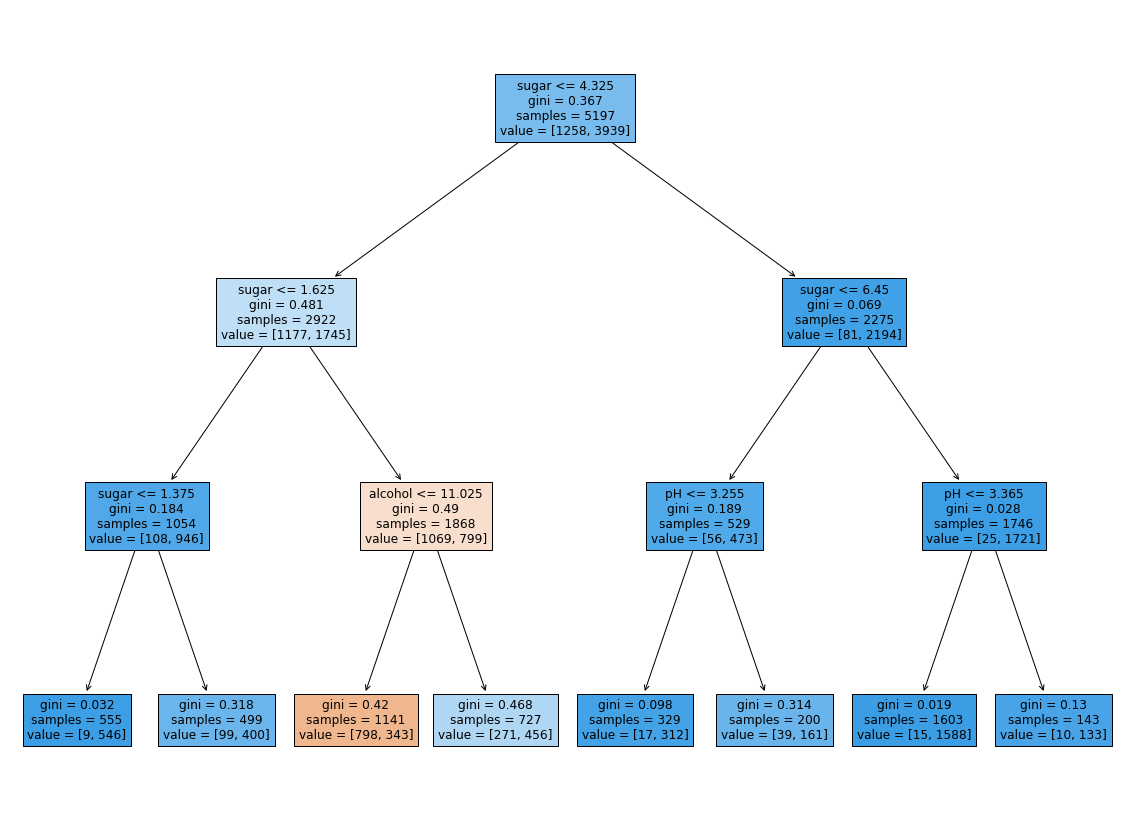
가지치기
과대적합을 방지하기 위한 것
max_depth
- 트리의 최대 깊이
- default = None
- 완벽하게 클래스 값이 결정될 때 까지 분할 또는 데이터 개수가 min_samples_split보다 작아질 때까지 분할
- 깊이가 깊어지면 과적합될 수 있으므로 적절히 제어 필요
1
2
3
4
| dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = 3, random_state=42)
dt.fit(train_input, train_target)
print(dt.score(train_input, train_target))
print(dt.score(test_input, test_target))
|
0.8454877814123533
0.8415384615384616
1
2
3
| plt.figure(figsize = (20, 15))
plot_tree(dt, filled = True, feature_names = ['alcohol', 'sugar', 'pH'])
plt.show()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import graphviz
from sklearn import tree
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(dt, out_file=None,
feature_names = ['alcohol', 'sugar', 'pH'],
filled=True)
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data, format="png")
graph
|

1
| graph.render("decision_tree_graphivz")
|
'decision_tree_graphivz.png'
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap, to_rgb
import numpy as np
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
artists = plot_tree(dt, filled = True,
feature_names = ['alcohol', 'sugar', 'pH'])
colors = ['blue', 'red']
for artist, impurity, value in zip(artists, dt.tree_.impurity, dt.tree_.value):
r, g, b = to_rgb(colors[np.argmax(value)])
f = impurity * 2
artist.get_bbox_patch().set_facecolor((f + (1-f)*r, f + (1-f)*g, f + (1-f)*b))
artist.get_bbox_patch().set_edgecolor('black')
plt.show()
|