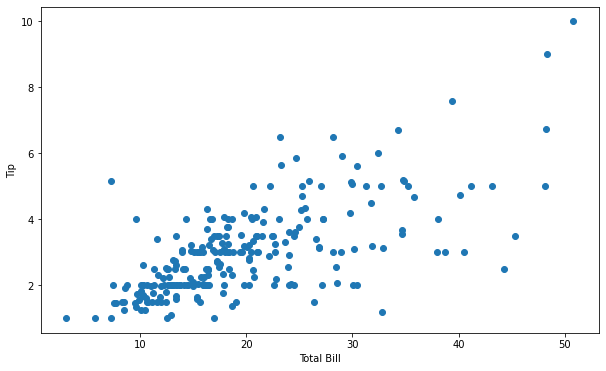
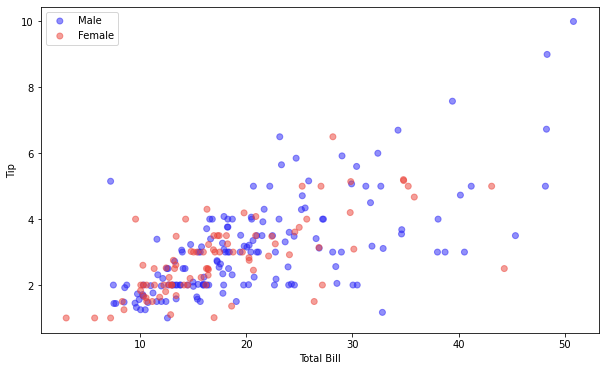
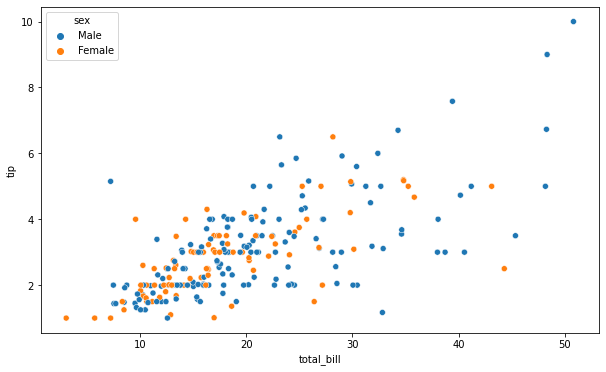
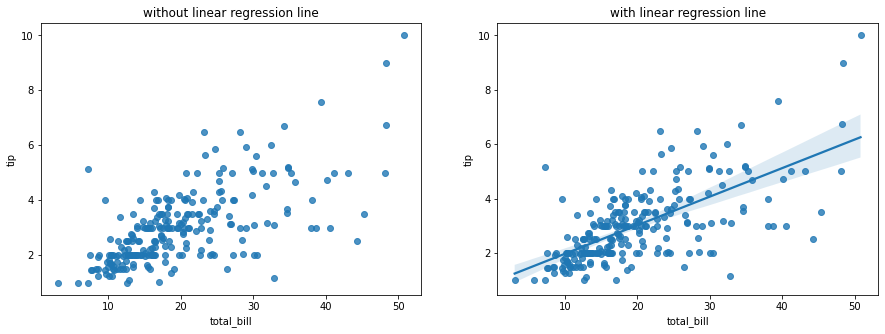
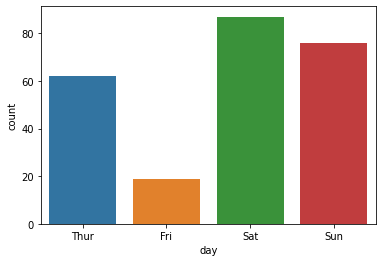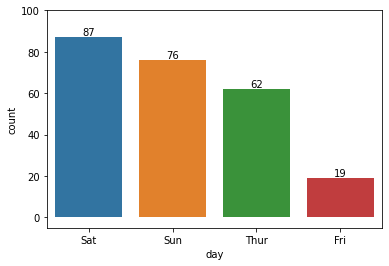라이브러리 불러오기
- pandas 라이브러리 불러오기, supermarket_sales.csv 파일 불러오기
1 | import pandas as pd |
Mounted at /content/drive
1 | DATA_PATH = "/content/drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/data/supermarket_sales.csv" |
| Invoice ID | Branch | City | Customer type | Gender | Product line | Unit price | Quantity | Date | Time | Payment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 750-67-8428 | A | Yangon | Member | Female | Health and beauty | 74.69 | 7 | 1/5/2019 | 13:08 | Ewallet |
| 1 | 226-31-3081 | C | Naypyitaw | Normal | Female | Electronic accessories | 15.28 | 5 | 3/8/2019 | 10:29 | Cash |
| 2 | 631-41-3108 | A | Yangon | Normal | Male | Home and lifestyle | 46.33 | 7 | 3/3/2019 | 13:23 | Credit card |
| 3 | 123-19-1176 | A | Yangon | Member | Male | Health and beauty | 58.22 | 8 | 1/27/2019 | 20:33 | Ewallet |
| 4 | 373-73-7910 | A | Yangon | Normal | Male | Sports and travel | 86.31 | 7 | 2/8/2019 | 10:37 | Ewallet |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 995 | 233-67-5758 | C | Naypyitaw | Normal | Male | Health and beauty | 40.35 | 1 | 1/29/2019 | 13:46 | Ewallet |
| 996 | 303-96-2227 | B | Mandalay | Normal | Female | Home and lifestyle | 97.38 | 10 | 3/2/2019 | 17:16 | Ewallet |
| 997 | 727-02-1313 | A | Yangon | Member | Male | Food and beverages | 31.84 | 1 | 2/9/2019 | 13:22 | Cash |
| 998 | 347-56-2442 | A | Yangon | Normal | Male | Home and lifestyle | 65.82 | 1 | 2/22/2019 | 15:33 | Cash |
| 999 | 849-09-3807 | A | Yangon | Member | Female | Fashion accessories | 88.34 | 7 | 2/18/2019 | 13:28 | Cash |
1000 rows × 11 columns
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-5de646d0-967f-4dc5-a51f-d7ef279760fb button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-5de646d0-967f-4dc5-a51f-d7ef279760fb');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | sales.info() |
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 1000 entries, 0 to 999
Data columns (total 11 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Invoice ID 1000 non-null object
1 Branch 1000 non-null object
2 City 1000 non-null object
3 Customer type 1000 non-null object
4 Gender 1000 non-null object
5 Product line 1000 non-null object
6 Unit price 1000 non-null float64
7 Quantity 1000 non-null int64
8 Date 1000 non-null object
9 Time 1000 non-null object
10 Payment 1000 non-null object
dtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(9)
memory usage: 86.1+ KB
Groupy by
- (동의어) 집계함수를 배운다.
1 | sales['Invoice ID'].value_counts() |
750-67-8428 1
642-61-4706 1
816-72-8853 1
491-38-3499 1
322-02-2271 1
..
633-09-3463 1
374-17-3652 1
378-07-7001 1
433-75-6987 1
849-09-3807 1
Name: Invoice ID, Length: 1000, dtype: int64
1 | sales.groupby('Customer type')['Quantity'].sum() |
Customer type
Member 2785
Normal 2725
Name: Quantity, dtype: int64
1 | sales.groupby(['Customer type', 'Branch', 'Payment'])['Quantity'].sum() |
Customer type Branch Payment
Member A Cash 308
Credit card 282
Ewallet 374
B Cash 284
Credit card 371
Ewallet 269
C Cash 293
Credit card 349
Ewallet 255
Normal A Cash 264
Credit card 298
Ewallet 333
B Cash 344
Credit card 228
Ewallet 324
C Cash 403
Credit card 194
Ewallet 337
Name: Quantity, dtype: int64
-
1 | print(type(sales.groupby(['Customer type', 'Branch', 'Payment'])['Quantity'].sum())) |
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
1 | sales.groupby(['Customer type', 'Branch', 'Payment'], as_index=False)['Quantity'].agg(['sum', 'mean']).reset_index() |
| Customer type | Branch | Payment | sum | mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Member | A | Cash | 308 | 5.500000 |
| 1 | Member | A | Credit card | 282 | 5.755102 |
| 2 | Member | A | Ewallet | 374 | 6.032258 |
| 3 | Member | B | Cash | 284 | 5.358491 |
| 4 | Member | B | Credit card | 371 | 5.888889 |
| 5 | Member | B | Ewallet | 269 | 5.489796 |
| 6 | Member | C | Cash | 293 | 4.966102 |
| 7 | Member | C | Credit card | 349 | 5.816667 |
| 8 | Member | C | Ewallet | 255 | 5.100000 |
| 9 | Normal | A | Cash | 264 | 4.888889 |
| 10 | Normal | A | Credit card | 298 | 5.418182 |
| 11 | Normal | A | Ewallet | 333 | 5.203125 |
| 12 | Normal | B | Cash | 344 | 6.035088 |
| 13 | Normal | B | Credit card | 228 | 4.956522 |
| 14 | Normal | B | Ewallet | 324 | 5.062500 |
| 15 | Normal | C | Cash | 403 | 6.200000 |
| 16 | Normal | C | Credit card | 194 | 5.105263 |
| 17 | Normal | C | Ewallet | 337 | 6.017857 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-06183b9d-9668-4956-b5b7-bf3ab9256622 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-06183b9d-9668-4956-b5b7-bf3ab9256622');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | print(type(sales.groupby(['Customer type', 'Branch', 'Payment'])['Quantity'].agg(['sum', 'mean']))) |
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
결측치 다루기
결측치 데이터 생성
1 | import pandas as pd |
| Score_A | Score_B | Score_C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80.0 | 30.0 | NaN |
| 1 | 90.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 |
| 2 | NaN | NaN | 80.0 |
| 3 | 80.0 | NaN | 90.0 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-19e2d3df-d166-4556-96a3-7e87c689f899 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-19e2d3df-d166-4556-96a3-7e87c689f899');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | df.isnull().sum() |
Score_A 1
Score_B 2
Score_C 1
dtype: int64
1 | df.fillna("0") |
| Score_A | Score_B | Score_C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80.0 | 30.0 | 0 |
| 1 | 90.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 80.0 |
| 3 | 80.0 | 0 | 90.0 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-8fdcaeb0-1a6d-42b3-a659-2ed1ac98f3c4 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-8fdcaeb0-1a6d-42b3-a659-2ed1ac98f3c4');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | df.fillna(method="pad") |
| Score_A | Score_B | Score_C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80.0 | 30.0 | NaN |
| 1 | 90.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 |
| 2 | 90.0 | 45.0 | 80.0 |
| 3 | 80.0 | 45.0 | 90.0 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-0beb1959-e8a4-4550-b78e-1da677eaf1f7 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-0beb1959-e8a4-4550-b78e-1da677eaf1f7');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | dict_01 = { |
| 성별 | Salary | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 남자 | 30 |
| 1 | 여자 | 45 |
| 2 | NaN | 90 |
| 3 | 남자 | 70 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-cd4f0fa9-4594-42f6-b011-ec8d9c313a45 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-cd4f0fa9-4594-42f6-b011-ec8d9c313a45');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | df['성별'].fillna("성별 없음") |
0 남자
1 여자
2 성별 없음
3 남자
Name: 성별, dtype: object
- 결측치
–> 문자열 타입이랑 / 숫자 타입이랑 접근 방법이 다름
–> 문자열 (빈도 –> 가장 많이 나타나는 문자열 넣어주기!, 최빈값)
–> 숫자열 (평균, 최대, 최소, 중간, 기타 등등..)
1 | import pandas as pd |
| Score_A | Score_B | Score_C | Score_D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80.0 | 30.0 | NaN | 50 |
| 1 | 90.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 | 30 |
| 2 | NaN | NaN | 80.0 | 80 |
| 3 | 80.0 | 60.0 | 90.0 | 60 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-4285262a-db62-49be-9c8d-273186ab08c4 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-4285262a-db62-49be-9c8d-273186ab08c4');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | df.dropna(axis = 1) |
| Score_D | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 50 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 80 |
| 3 | 60 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-0e190d15-cdf3-464b-bcfb-9ef6867cfba1 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-0e190d15-cdf3-464b-bcfb-9ef6867cfba1');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | df.dropna(axis = 0) |
| Score_A | Score_B | Score_C | Score_D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 | 30 |
| 3 | 80.0 | 60.0 | 90.0 | 60 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-c4cae1e4-71a0-446b-8e51-6af06230d2ee button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-c4cae1e4-71a0-446b-8e51-6af06230d2ee');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
이상치
1 | sales |
| Invoice ID | Branch | City | Customer type | Gender | Product line | Unit price | Quantity | Date | Time | Payment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 750-67-8428 | A | Yangon | Member | Female | Health and beauty | 74.69 | 7 | 1/5/2019 | 13:08 | Ewallet |
| 1 | 226-31-3081 | C | Naypyitaw | Normal | Female | Electronic accessories | 15.28 | 5 | 3/8/2019 | 10:29 | Cash |
| 2 | 631-41-3108 | A | Yangon | Normal | Male | Home and lifestyle | 46.33 | 7 | 3/3/2019 | 13:23 | Credit card |
| 3 | 123-19-1176 | A | Yangon | Member | Male | Health and beauty | 58.22 | 8 | 1/27/2019 | 20:33 | Ewallet |
| 4 | 373-73-7910 | A | Yangon | Normal | Male | Sports and travel | 86.31 | 7 | 2/8/2019 | 10:37 | Ewallet |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 995 | 233-67-5758 | C | Naypyitaw | Normal | Male | Health and beauty | 40.35 | 1 | 1/29/2019 | 13:46 | Ewallet |
| 996 | 303-96-2227 | B | Mandalay | Normal | Female | Home and lifestyle | 97.38 | 10 | 3/2/2019 | 17:16 | Ewallet |
| 997 | 727-02-1313 | A | Yangon | Member | Male | Food and beverages | 31.84 | 1 | 2/9/2019 | 13:22 | Cash |
| 998 | 347-56-2442 | A | Yangon | Normal | Male | Home and lifestyle | 65.82 | 1 | 2/22/2019 | 15:33 | Cash |
| 999 | 849-09-3807 | A | Yangon | Member | Female | Fashion accessories | 88.34 | 7 | 2/18/2019 | 13:28 | Cash |
1000 rows × 11 columns
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-6f6e6109-861d-4be9-ba85-95e41759ab5e button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-6f6e6109-861d-4be9-ba85-95e41759ab5e');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
일반적인 통계적인 공식
IQR - 박스플롯 - 사분위수
Q0(0), Q1(25%), Q2(50%), Q3(75%), Q4(100%)
이상치의 하한 경계값 : Q1 - (1.5 * (Q3-Q1))
이상치의 상한 경계값 : Q3 + (1.5 * (Q3-Q1))
도메인(각 비즈니스 영역, 미래 일자리)에서 바라보는 이상치 기준(관습)
1 | sales[['Unit price']].describe() |
| Unit price | |
|---|---|
| count | 1000.000000 |
| mean | 55.672130 |
| std | 26.494628 |
| min | 10.080000 |
| 25% | 32.875000 |
| 50% | 55.230000 |
| 75% | 77.935000 |
| max | 99.960000 |
<script>
const buttonEl =
document.querySelector('#df-9b6fc1ab-b0b3-47ba-b180-b37f4ec43d85 button.colab-df-convert');
buttonEl.style.display =
google.colab.kernel.accessAllowed ? 'block' : 'none';
async function convertToInteractive(key) {
const element = document.querySelector('#df-9b6fc1ab-b0b3-47ba-b180-b37f4ec43d85');
const dataTable =
await google.colab.kernel.invokeFunction('convertToInteractive',
[key], {});
if (!dataTable) return;
const docLinkHtml = 'Like what you see? Visit the ' +
'<a target="_blank" href=https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/data_table.ipynb>data table notebook</a>'
+ ' to learn more about interactive tables.';
element.innerHTML = '';
dataTable['output_type'] = 'display_data';
await google.colab.output.renderOutput(dataTable, element);
const docLink = document.createElement('div');
docLink.innerHTML = docLinkHtml;
element.appendChild(docLink);
}
</script>
</div>
1 | Q1 = sales['Unit price'].quantile(0.25) |
1 | print(sales['Unit price'][~(outliers_q1 | outliers_q3)]) |
0 74.69
2 46.33
3 58.22
6 68.84
7 73.56
...
991 76.60
992 58.03
994 60.95
995 40.35
998 65.82
Name: Unit price, Length: 500, dtype: float64